₋Identify and differentiate between common radiology modalities:
₋Develop a basic understanding of advanced or emerging modalities
₋Introduce with inventors of Radiological Modalities
Radiology
Radiology is a department of medical imaging which deals to diagnose and treatment of disease within the human as well as animals.
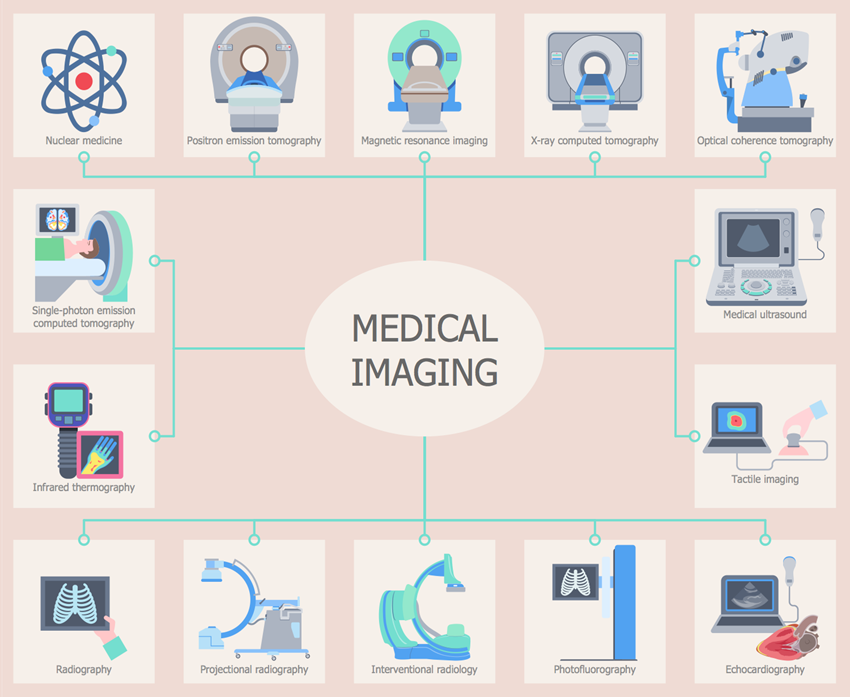
There are different kind of modalities which is present in radiology department such as x-ray, ultrasound, ct, mri, dexa, mammography, fluroscopy, PET Scan, DSA, etc. In medical imaging, the mention modalities can able to see through a body like bones, muscles, arteries, veins, blood and fluids.
The department consist of following members
- Receptionist – Patient can take appointments, pay bills and ask for any query you have
- Nursing Staff – At radiology department, nurses are there for check peripheral i.v.s, monitor vital signs, medications and even help the patient in their needs.
- Radio-Technologist – RT are the person who perform the scan, evaluate patient health status and give brief explanation about procedure. Radiologist – They are the doctors who specialized in diagnosis and interpret the radiographs.
X-Ray Pioneers
- H. C. Snook – Developed the interrupter less transformer
- William Coolidge – Designed the “Hot Cathode” X-ray tube
- Roentgen – Used a glass plate coated with a photographic emulsion, created first Radiograph
- Michael Idvorsky Pupin – Demonstrated the radiographic use of fluorescent screens (intensifying screens)
- Thomas Edison – Invented first fluoroscope and discovered many of the fluorescent chemicals used today
- Dally – Serving as a subject for many of Edison’s X-ray experiments, severely burned his arms, had to be amputated, and in 1904 he died from his exposure, first recorded X-ray fatality in the United States
- George Eastman -Invented photographic film using cellulose nitrate
Father of X-Rays
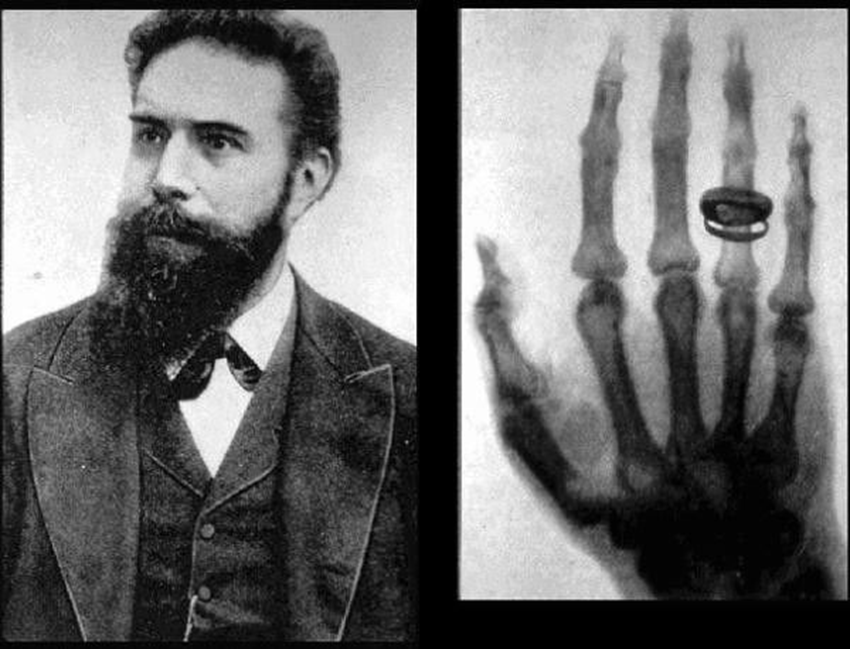
X-RAY are discovered by Sir Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen on 8November,1895
It was an unknown ray so Sir Roentgen coined it as X-RAY.
It was discovered when he was working on his laboratory and he saw some fluoroscent green light appearance and a shadow of hard object. Later he put his wife madam Berta’s hand in which she wore her wedding ring on a photographic plate and expose it and that was his first radiograph.
Sir Roentgen was awardeed the first nobel prize in physics in 1901 for his discovery. When asked what his thoughts were at the moment of discovery, he replied “I didn’t think, I investigated”. He never took out any patent on x-rays, to ensure that the world could freely benefit from his work.
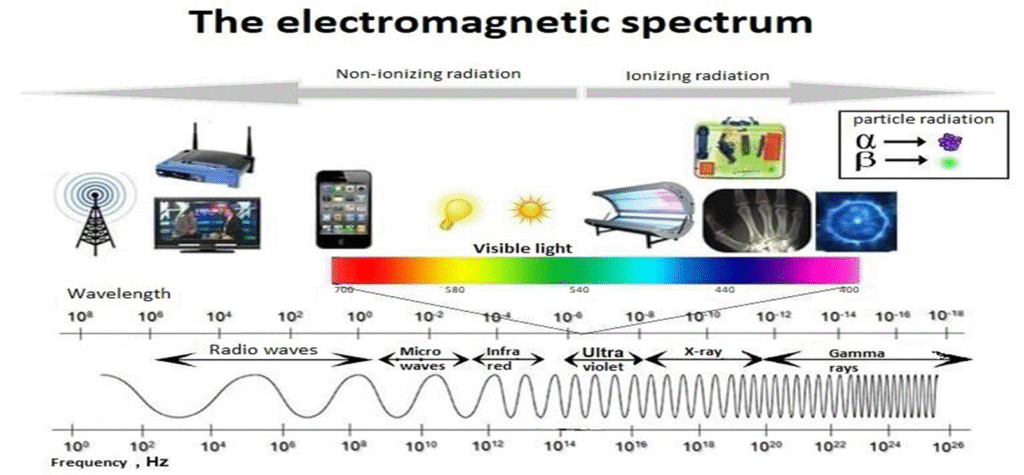
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Overview About Modalites
1.X-RAY
These are the highly penetrating form of energy
It’s energy in range 124eV to 124keV
It is used in medical diagnosis like X-ray, CT, Fluroscopy, Radiotherapy.
It is also used in security purpose, Cosmetic Surgery

2. Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a sound wave which is higher frequency than audible human hearing sound
Ian Donald introduced ultrasound in diagnostic and medicine in1956
Frequency range- more than 20kHz
It’s uses-
i. Medical Imaging such as obstetric usg, doppler scan and body parts of humans as well as animals.
ii.Field of communication
iii.Dermal treatments
3. COMPUTED RADIOGRAPHY-
CT is a medical imaging method which is used in radiology to get highly detailed internal raiographs of body.
Sir Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield invented CT Scanner
It’s uses-
- Medical purpose: Routine scans, Contrast Scans as well as Angiographic procedures
- Geological use
- Cultural heritage use
- Industrial use
4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
It is also used as a diagnostic purpose to obtain detailed image of anatomy as well as physiological process of the body.
1971 Sir Raymond Damadian invented MRI
In this modality, there is no radiation only magnetic fields are there.
It is more useful in imaging of soft tissue
It is widely use for medical purpose
Rather than diagnostic use it works in palaeontology, forensic imaging
5. DEXA
DEXA stands for Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry is used for measure bone mineral density.
The bone density scan was invented by the late Sir John R. Cameron
Two x-ray beams have different energy level are aimed at patient’s body.
It is used to diagnose osteoporosis and osteopenia
6. MAMMOGRAPHY
Mammography(mastography) deals with mammary gland examination which works on low energy x-rays.
In late 1950s Sir Robert Egan combine a technique of low kVp with high mAs and to devise a method of screening mammography
The aim of mammography is to identify early detection of unknown lesion or symptoms
Mammography is done at a particular age i.e. after 40
October month is known as Breast Cancer awarness month
7. FLUOROSCOPY
It is also a imaging modality that permits live x-ray imaging of patient.
In late 1890’s Thomas Alva Edison began investigate materials for ability to fluoresce and he had invented a fluroscope.
It allow to visualize functioning and movement of patient like swallowing, heart pumping action or motion, interventional radiology and image-guided surgery.
8. DSA
DSA stands for digital subtraction angiography which deals with blood vessels by subtracting bones and muscles.
DSA was invented by a group of medical physicits headed by Sir Charles A. Mistretta
It is useful in diagnosis and treatment of arterial and venous occulsions.
9. PET
Positron Emission tomography is a functional imaging technique that uses radiotracers to see and measure metabolic process like blood flow, chemical composition and absorption.
Sir Edward J. Hoffman with Michael E. Phelps invented PET scanner which helps in detection of cancer, heart disease and other severe illness
Radiotracer induce in patient’s body and then it emit gamma rays which is detect by PET scanner