What is Dark Room
• Term “darkroom” overstates the case
• White light is EXCLUDED.
• Important place in the radiology department of a hospital, clinic, nursing home or a private x-ray clinic. Is a room where the latent image is processed into visible image by means of chemical processing. Hence also called processing room.
BASIC FUNCTION OF DARK ROOM
• Storage – of unexposed films
• Film processing
• Handling of films
•Loading and unloading the film
Dark Room Construction
•Location
•Size and installation
•Building Essentials
A. protection against radiation
B. floor
C. Wall covering
•Ventilation
•Electrical wiring
• Hatches
•Entrance
•Illumination
•Dry side Wet side
Location
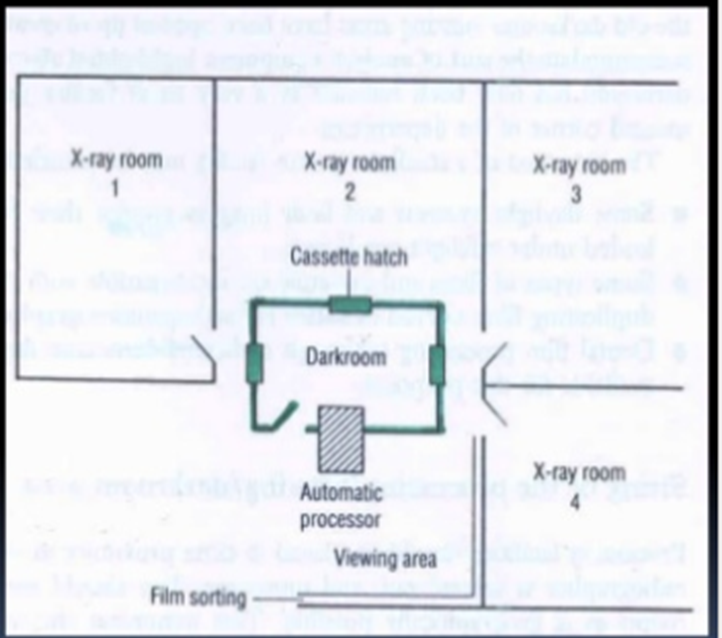
•Centrally located
•Close to radiographic room- time saving
•Away from hot, damp basement areas.
•Serviced by hatches from the adjacent imaging room
•Accessible in terms of water and power supply
•Adjoining viewing room
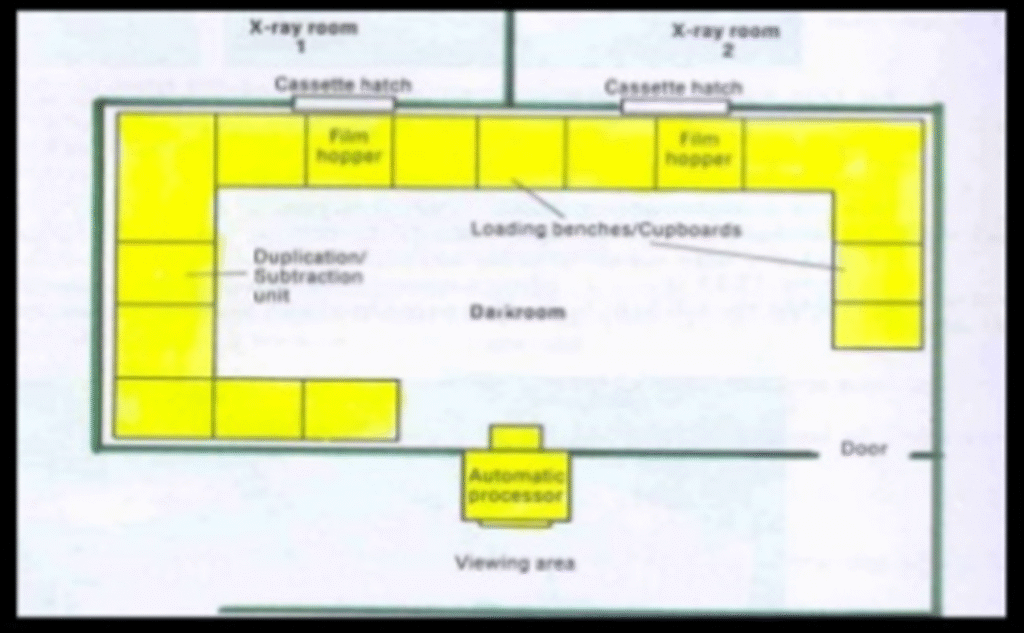
Size & Installation
•Large enough to accommodate all necessary equipments without crowding.
•Parameters of an ideal dark room-
• floor space- 100 sq.feet
• Ceiling height- 11 feet
•Size can vary depending on the department needs.
•Safe distance between dry and wet side. Loading bench and processing tank on opposite sides.
Building Essential
A. PROTECTION AGAINST RADIATION
•Essential-to prevent film fogging
Walls being lined by- lead sheet or lead equivalent material
• 1.5 mm or 1.6 mm lead mostly used.
•Alternative- solid concrete wall construction- 15cm thick
•It leads to sufficient work upto 100kV.
B. Floor
•non- porous
• non- slippery
• chemical resistant
• stain proof
• durable & easy maintenance
• Light colored
• satisfactory material- ceramic tiles of porcelain
natural clay
Asphalt tiles
• unsuitable materials- ordinary linoleum and concrete
C. WALLS/CEILING
• do NOT have to be dark.
• color judged under safe light illumination- ensure maximum
• reflection into working surface.
• covering with chemical resistant materials-special
paint, varnish, concrete or ceramic tiles
• easy to wipe/clean
VENTILATION

•Window avoided
•Relative humidity maintained- 40-60%,room temp- 18-20 degree Celsius.
•Ideal solution- good air conditioning system Alternative –extractor fan- creates positive air pressure.
Electrical Wiring
•Electric shock is dangerous- as close proximity with
•chemical tanks
•Water pipes
•Damp floors
•Wet fingers Prevention- proper earthing .
Pass Box
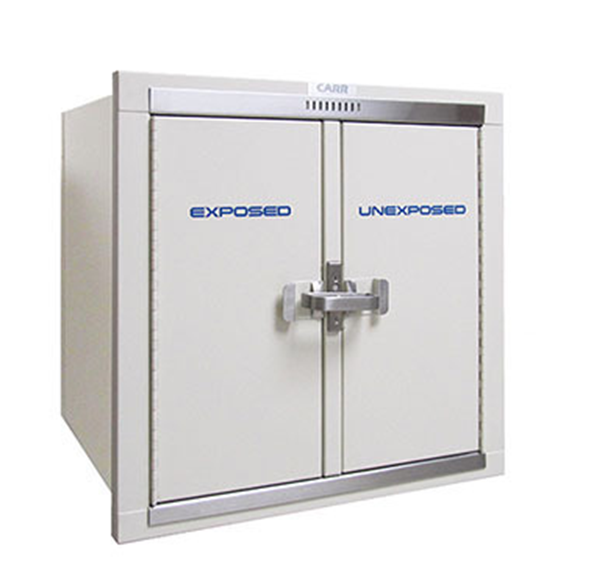

•Designed – to transfer film cassettes to and from the dark room without radiation light entering.
•Include 2 compartments-
Exposed
unexposed
•Metallic structures with lead lining- x-ray shielding
•Typically wall mounted
•Near film loading bench
•Include x-ray proof automatic interlocks, closes one door when other is opened.
• provides temporary storage of loaded cassettes.
Entrance
•There are following types of entrance used in dark rooms-
A. Single door-
•simplest type of entrance
•Single door- light tight & radiation proof An inside lock
B. DOUBLE DOOR
• having 2 doors
• one leading IN
• other used for OUT
C. MAZE TYPE
elaborate type of entrance
• NO requirement of door
• serves as a light trap
• High cost
• Large space occupying
• Rarely used these days.
D. REVOLVING DOOR
• Occupies very little space
• convenient light proof access to dark room
• echo- friendly
ILLUMINATION
The dark room should have 2 types of illumination-
- General illumination/white lighting
- Safe light/radiographic illumination
General Illumination
used for
- Inspection & maintenance of cassette and screen
- Cleaning of work space
- Servicing of equipment
- Sited close to ceiling- avoids strong shadow
- Moderate in intensity
- Centrally placed
- More than one switch preferable &
- Identification of such switches is important
Safe Light
2 types
direct – distance: 1.2m from working surface
indirect- distance: 2.1m from floor
•Provide adequate illumination without fogging films.
•Have filters of proper colors(red filters can be used for both blue and green sensitive films)
•Working distance- not less than 1.2 m.
•Bulb wattage- d less than 15 watts. I – 25 watt
•Work quick under it.
•Not completely safe, prolonged exposure- fogging of films
Dry Side
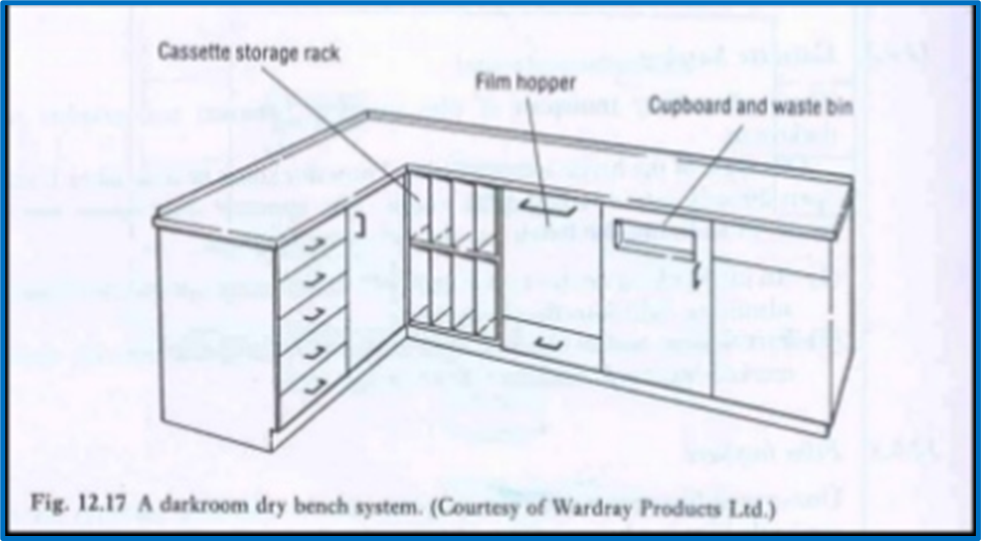
•Components comprises of-
•Loading bench
•Compartment for cassettes
•Film bin
•Storage for reserve film
•Brackets for film hangers
•Wastepaper receptacle
Wet Side
•Processing tank-simplest type has 4 compartments-
• 1. developing
• 2. rinsing
• 3. fixing
• 4.washing tank
stainless steel of alloy- generally used material.
•Processing chemicals
•2 stirring paddlers
•Thermometer
•Washing tank
•Dryers
Chemicals used in Compartments
DEVELOPERS
- Organic reducing agent – hydroquinone , metol
- Activating agent – sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide
- Stainer – sodium bromide, sodium iodide
- Preservative – sodium sulphite
Why they used
- hydroquinone (for high contrast)
- metol ( for low contrast) “N-methyl-p-aminophenol“
- sodium sulfite, to reduce the oxidation rate of developer and dissolve the products into sulfonates (colourless) thereby increasing its life
- Activating agent to maintain the pH (at 10-11) of the solution for optimum work of developer
- Restrainer – potassium bromide, prevents the developer from acting on unexposed silver (thus preventing fog formation)re
Fire Safety
•Ideally all darkrooms should be provided with fire exits
•Clearly indicated
•Left unobstructed at all the times

